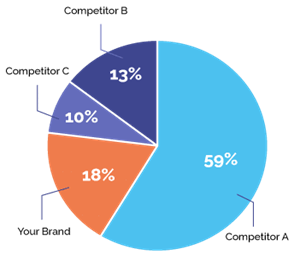
In today’s fiercely competitive business environment, market share has become one of the golden indicators of brand success. For businesses, a profound understanding of market share is crucial, with both relative market share and market penetration rate playing pivotal roles in brand decision-making. These two concepts not only reveal the brand’s position in the overall market but also provide critical insights, helping businesses formulate precise strategies for sustainable development. Let’s explore the intricacies of relative market share and market penetration rate, and how they collaboratively pave the path to brand success.
Market Share: The Cornerstone of Brand Positioning
Market share refers to the proportion of sales of a particular brand or product in a specific market compared to the total market sales. This metric not only directly reflects the brand’s position in the industry and the size of its market share but also serves as a crucial foundation for strategic planning and market decisions.
- Formula for Market Share:

- Example: If a brand’s annual sales in a specific market are $10 million, and the total market sales are $200 million, then the market share of that brand is

This implies that the brand holds a 5% share in that market.
Relative Market Share: Gauge of Competitive Prowess
Relative market share is a crucial metric for gauging the brand’s relative strength in competition. This metric not only provides insight into the brand’s position in the market but also offers substantial support for strategic decision-making.
- Formula for Relative Market Share:

- Example: Taking an electronics brand as an example, if the brand’s sales share in a specific market is 20%, and the largest competitor’s sales share is 15%, the relative market share for the brand is
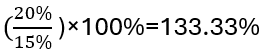
This indicates that the brand has a stronger competitive position relative to the largest competitor in the market.
This metric not only provides insight into the brand’s position in the market but also offers substantial support for strategic decision-making. When the relative market share is high, businesses can confidently formulate pricing strategies, indicating a leading position in the competitive landscape. Additionally, a high relative market share prompts consideration of increased investment in advertising and promotional activities to solidify or expand market share.
Market Penetration Rate: Navigating Market Depth:
Market penetration rate is a key indicator of the brand’s penetration level in the overall market. This metric provides businesses with an opportunity to expand market share by developing new market segments to increase sales.
- Formula for Market Penetration Rate:
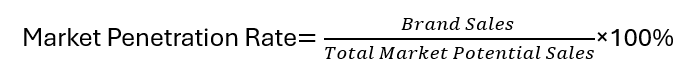
- Example: Consider a tech accessories brand with annual sales of $8 million in a market where the total potential sales for such products amount to $100 million. Calculating the market penetration rate:

This signifies a penetration depth of 8% in the tech accessories market. The brand can capitalize on this by exploring new customer segments or introducing innovative products, presenting an opportunity to expand its market share. Understanding this penetration rate guides strategic decisions for sustained growth in the competitive tech industry.
Navigating the Competitive Landscape
Understanding both relative market share and market penetration rate directly guides our actions in the market. In our pricing strategy, we consider the impact of relative market share to ensure our prices remain competitive while increasing profitability. Simultaneously, by continuously increasing the market penetration rate, we expand our customer base, creating more possibilities for the brand’s future growth.
These two metrics are intertwined, serving as key drivers for successfully operating and developing a business. By consistently monitoring changes in market share, we can adjust strategies flexibly and stay attuned to market trends. In the journey of business competition, mastery of market share will be one of our ongoing driving forces.