Surveys have become an indispensable tool for gathering data and insights in various fields, from market research to scientific studies. Their advantages over traditional methods are numerous, including cost-effectiveness, wide coverage, and efficiency. However, many people perceive surveys as mere collections of questions that respondents fill out. Designing a survey plays a pivotal role in determining the accuracy of its results. This article explores the science behind survey design, emphasizing the critical factors that can make or break the quality of survey data.
Defining Your Research Purpose
Before embarking on survey design, it is imperative to clearly define your research purpose and the core questions you intend to address. Every question should be directly related to your research objectives. The selection of the types of response options is equally vital. Choices can range from categorical and metric to open-ended. Categorical responses often lend themselves to straightforward percentage comparisons, while metric options enable a wide array of analyses, including regression and hypothesis testing.
Structuring Your Survey
The structure of your survey matters significantly. A well-structured survey can keep respondents engaged and provide meaningful results. Begin with general or simple questions to ease participants into the survey and ensure clarity and ease of comprehension. More complex questions should be placed further along in the survey. Grouping questions related to similar topics or formats together can enhance the survey’s visual coherence.
The Art of Questioning
When it comes to crafting survey questions, there are several key principles to keep in mind. First, formulate neutral questions. Avoid any emotionally charged language that could lead to biased responses. Keep question’s objective to allow respondents to provide honest feedback.
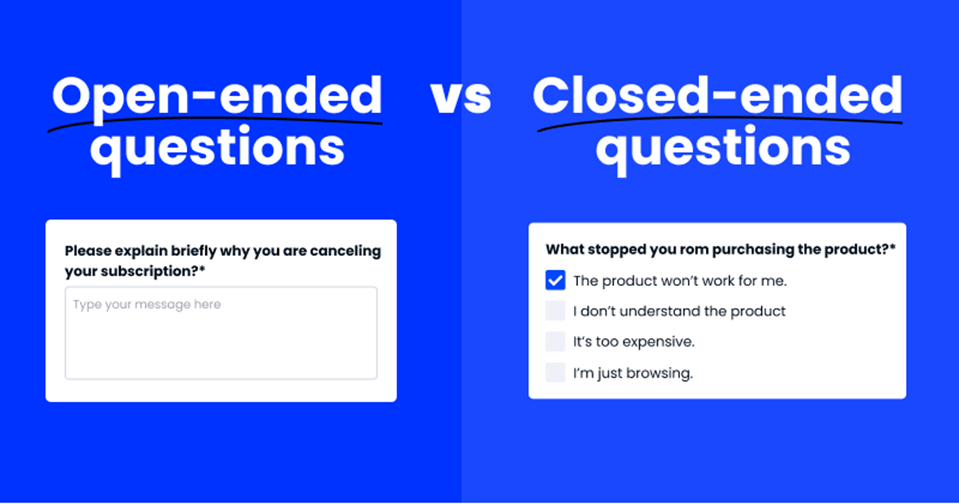
Introduce open-ended questions judiciously. They offer valuable qualitative insights but can be time-consuming to analyze. Balancing their use with closed-ended questions is crucial.
Avoid question overload. A lengthy survey can quickly overwhelm and disinterest respondents, leading to survey abandonment. Prioritize the most critical questions to maintain respondent engagement.
Consider Diversity in Your Audience
One of the paramount considerations in survey design is the diversity of your target audience. Ensuring your response options are comprehensive and steering clear of potentially confusing language is essential. Recognize that different individuals may interpret questions differently based on their background, experiences, and cultural factors. Strive for clarity and inclusivity to make your survey accessible to a broad range of respondents.
In conclusion, surveys are more than just a series of questions; they are a complex science that demands careful planning and execution. Designing an effective survey involves defining research objectives, selecting the right response options, structuring questions logically, and considering the needs of diverse respondents. The quality of survey data can significantly impact the validity of your research findings. In the era of data-driven decision-making, understanding the science of survey design is essential for ensuring the reliability and relevance of the insights you collect.