After consumers make a purchase, the story doesn’t end there. In fact, it’s just the beginning of the decision-making process. Following the purchase decision, consumers face a series of subsequent processes that directly influence their perceptions, attitudes, and future buying decisions regarding the product. Understanding and managing these processes are crucial for businesses because they can impact consumer satisfaction, loyalty, and reputation. Let’s delve deeper into these processes.
Post-Purchase Dissonance
Post-purchase dissonance, where consumers experience doubt or anxiety about the rationality of their decision after buying a product or service, is a common phenomenon. To illustrate, let’s consider a recent event. On February 4, 2024, Miami International held a highly anticipated Messi exhibition match in Hong Kong. However, to the disappointment of the audience, Messi failed to appear as expected.
Prior to the event, the organizers explicitly advertised that, according to the contract with Miami International, Messi would appear and participate for 45 minutes. However, when the match began, Messi was absent from the field. This sudden turn of events sparked anger and protests from the Hong Kong audience, who demanded a refund of their ticket fees. Faced with dissatisfaction and condemnation from the audience, the organizers ultimately agreed to refund 50% of the ticket fees.
This event vividly illustrates the importance of post-purchase evaluation. The audience expected to witness Messi’s match when purchasing tickets, but the reality fell far short of expectations. This disparity fueled their dissatisfaction and protests, ultimately leading to refund requests. For the organizers, the loss was not only the 50% ticket fees but, more importantly, the loss of trust and loyalty from the audience. This event may have a long-term impact on Miami International’s activities and brand image in Hong Kong.
The key to addressing post-purchase dissonance lies in providing effective after-sales support and solutions to help consumers alleviate anxiety and rebuild trust. In this event, if the organizers could communicate timely and provide reasonable explanations, as well as offer appropriate compensation or solutions to the affected audience, it might mitigate their dissonance and maintain a good relationship with consumers. This measure is crucial for the future activities and brand image restoration of Miami International.
Buyer Learning
Consumers continue to learn after making a purchase. They accumulate new knowledge and experiences through product/service usage, interactions with others, and information gathering, which directly influence their future buying behavior.
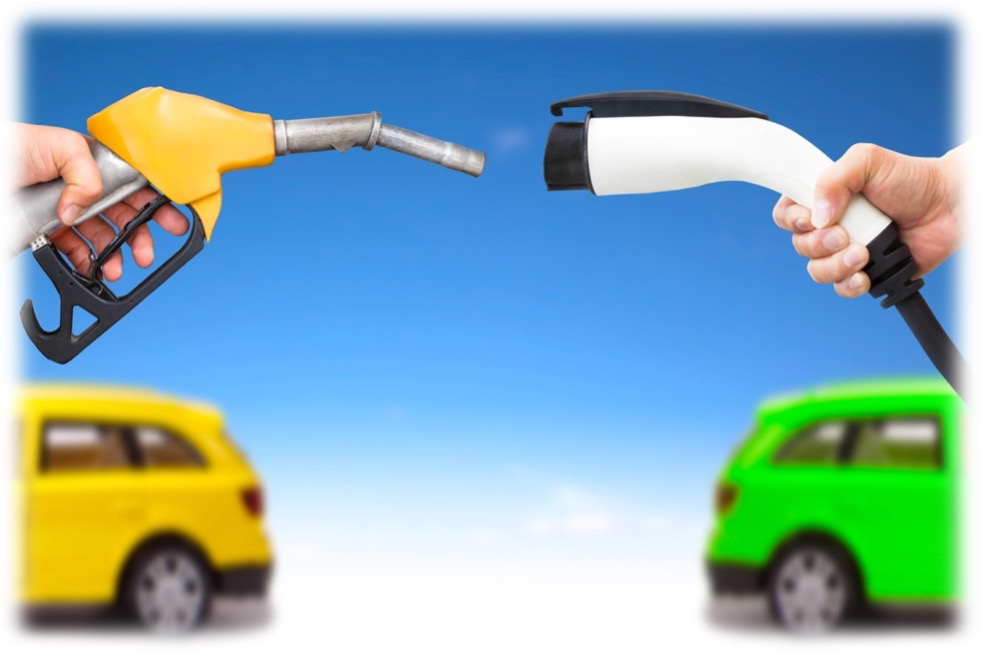
Suppose a consumer purchases a new electric car. Initially, they may be curious about the vehicle’s performance, battery life, and charging facilities. Therefore, they may read articles, watch videos, and exchange experiences with other electric car owners.
However, the consumer’s learning process may be influenced by biases. If they initially hold a very positive attitude towards electric cars, believing them to be environmentally friendly and energy-efficient, they may be more inclined to notice these advantages during the learning process and overlook potential drawbacks, such as longer charging times or inconvenient charging facilities.
On the other hand, if the consumer is overly confident that they already know all about electric cars, they may be less willing to seek external opinions or advice. Even if others present viewpoints contrary to their own, they may believe their own views are correct and choose to ignore these differing opinions.
While consumers may gain more knowledge and experience about electric cars through learning after the purchase, it’s essential to recognize that confirmation biases and overconfidence may affect the objectivity and effectiveness of learning. By maintaining an open mind and accepting information and opinions from different sources, consumers can better utilize the learning process and make wiser decisions.
Consumer satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a product is a crucial factor that directly shapes their attitude towards the brand and future purchasing behavior. Satisfied consumers often choose to repurchase products from the same brand, gradually building brand loyalty and driving more sales through positive word-of-mouth. However, if consumers are dissatisfied with a product, they may opt for returns or switch to competitors’ products.
Satisfied consumers are more likely to actively share their purchasing experiences with others, thereby increasing brand awareness and reputation, and subsequently driving more sales. However, dissatisfied consumers may express their dissatisfaction through various channels, including posting negative reviews on social media, leaving negative feedback online, or verbally complaining to friends and family.
Disposition
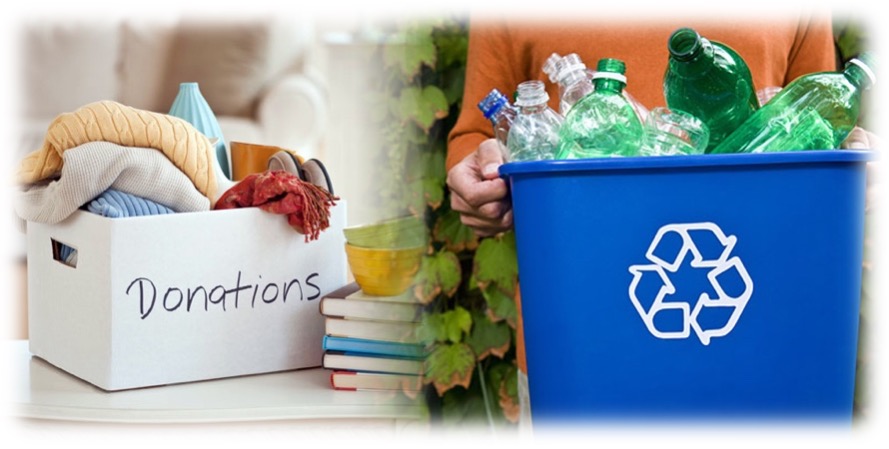
Finally, consumers may consider how to dispose of the product after use. The disposal method can involve physical or emotional detachment from the product, depending on individual logic, rationality, and circumstances. For example, one consumer may choose to recycle an old phone, while another may choose to donate it to a charity. Additionally, disposal methods may also be influenced by factors such as environmental awareness and social responsibility. For example, some consumers may prefer sustainable disposal methods, such as recycling or reusing, to reduce environmental impact.
Therefore, for businesses, understanding consumers’ disposal methods and motivations is crucial for maintaining brand image and promoting repeat purchases. By providing convenient disposal options, emphasizing environmental and social responsibility, businesses can enhance consumers’ favorability towards the brand and establish long-term brand loyalty.
Conclusion
After consumers purchase a product, a series of subsequent processes unfold. These include post-purchase dissonance, buyer learning, satisfaction/dissatisfaction, and disposition. These factors directly shape consumers’ attitudes towards the brand and influence their future buying behavior. Understanding and managing these post-purchase processes are crucial for businesses because they impact consumer satisfaction, loyalty, and reputation, ultimately affecting sales and brand image. By providing effective after-sales support and solutions, maintaining an open learning attitude, prioritizing consumer satisfaction, and addressing product disposal and environmental concerns, companies can enhance consumer awareness and favorability towards the brand, thereby fostering long-term brand loyalty and promoting sustainable growth.