Navigating Business Success Through Sales Data
In the age of digital transformation, understanding the significance of data has become paramount. This article delves into the importance of sales data, introduces its common types, and shares key insights into the proper analysis of this invaluable resource. By reading, you’ll gain a profound awareness of the potential within data, empowering you to make informed decisions on the business stage.
Introduction: The Complexity of Sales Data
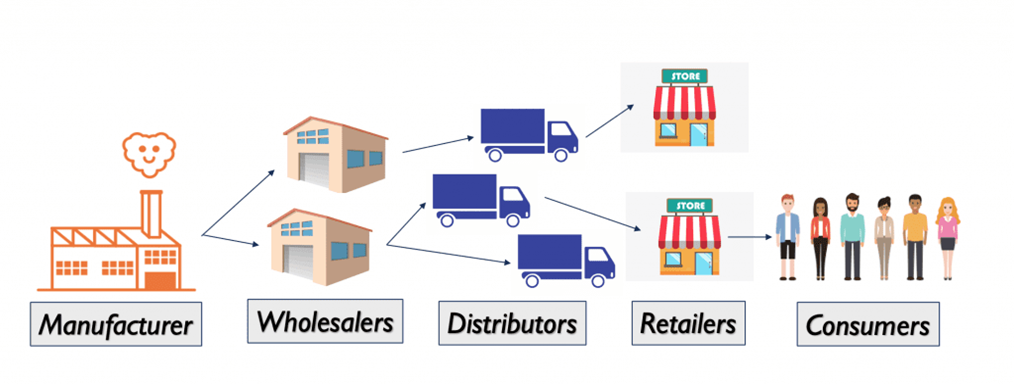
Sales data, seemingly simple on the surface, is a complex web of intricacies. Selling is not merely about delivering goods to customers; it involves a convoluted process. Before customers lay hands on their desired products, they go through a series of stages: manufacturers produce based on demand, products are handed to wholesalers, retailers acquire goods through distributors, and ultimately, the products are sold to customers. Every aspect of this multifaceted journey falls within the realm of sales data. From order amounts to growth rates and sales figures, these elements constitute the vibrant and diverse components of sales data.
The Three Key Types of Sales Data
Within this extensive dataset, three crucial types stand out: Manufacturer Sales Data, Intermediary Sales Data, and Retail Sales Data.
Manufacturer Sales Data: Considered one of the most accurate and comprehensive types of data, Manufacturer Sales Data originates directly from the source – the manufacturers themselves. This data focuses on the entire sales chain from the manufacturing stage to the initial wholesale. It encompasses the assessment of production scale, efficiency, and the initial sales of products. Manufacturers leverage this data to understand the popularity of their products in the market, enabling them to formulate precise production plans to meet market demands.
Intermediary Sales Data: Shifting focus to the middle of the supply chain – from manufacturers to retailers – Intermediary Sales Data includes information about product distribution, storage, and various other aspects. Intermediaries utilize this data to understand the smoothness of the supply chain, key information about on-time deliveries, and optimize logistics processes to enhance operational efficiency.
Retail Sales Data: Covering the entire process from wholesalers to retailers and finally to end customers, Retail Sales Data includes information about retail sales, inventory changes, promotional activities, and more. This data represents the actual purchases made by consumers, providing retailers with a profound understanding of product popularity, supporting optimized inventory management, and serving as the basis for targeted promotional strategies.

These three types of sales data intertwine to create a full picture, providing business leaders with comprehensive market awareness and decision-making support.
Before Analyzing: Clarifying Objectives and Ensuring Accuracy
Before diving into the analysis of sales data, it’s essential to clarify your objectives. What goals are you aiming to achieve through market data analysis? Whether it’s increasing product sales or understanding market trends and competitors’ sales situations, thorough research lays the foundation for effective sales strategies.
Choosing the right channels for obtaining sales data is crucial. Ensure data is sourced from reliable channels to guarantee accuracy and completeness. Different channels may provide varying data, so preliminary validation and cleaning of data are necessary before analysis.
Once data is obtained, tools like Excel and Tableau can facilitate visualization, making data more understandable and streamlining the process of data organization and analysis. Through in-depth data analysis, a better understanding of market dynamics and consumer demands can be achieved, allowing for the formulation of targeted sales strategies. The iterative process of data analysis, continuous monitoring, and adjustments contribute to the achievement of sales objectives.





